Fluorescence Digital Image Gallery
Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblast Cells
A fibroblast cell line established from a skin biopsy of an adult male, the Indian Muntjac deer epidermis line is commonly used in laboratories around the world, especially for chromosome studies. Members of the family Cervidae, Muntjacs are barking deer that emit their characteristic sound when they feel threatened or alarmed.
The normal (non-transformed) Indian Muntjac cell line is susceptible to the herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana strain), but is resistant to poliovirus 1. Recent tests have demonstrated that the cells produce both detectable bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) antigens and infectious BVDV virions. Muntjac cells are negative for reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes.
Cell lines derived from the Indian Muntjac have been of significant scientific interest primarily because the animal possesses the fewest number of diploid chromosomes of all mammals, with only six chromosomes in the female and seven in the male. Such a small number of chromosomes makes Indian Muntjac cells an ideal candidate for mitosis research. Moreover, in recent years, Indian Muntjac cells have gained a reputation for their usefulness as a model to study telomere biology. Telomeres, the regions of DNA that occur at the end of chromosomes, are at the center of many modern studies involving the aging of organisms and cell senescence. It is generally believed that the shortening of telomeres, which occurs during the division of most cells, is responsible for age-related cellular malfunction and death. Thus, telomeres are also of interest in regard to cancer, since tumor cells are often able to proliferate unhindered by the passage of time due to various mechanisms that avoid the shortening of chromosomal telomeres.
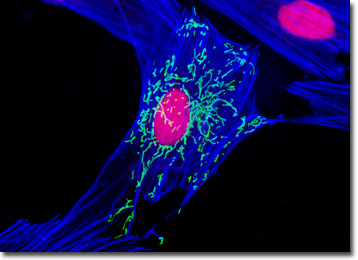
The culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin cells that is presented in the digital image above was labeled with SYTOX Orange and Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin, which target DNA and filamentous actin, respectively. In addition, the cells were transfected with a pEYFP-Mitochondria plasmid subcellular localization vector, thus localizing a yellow fluorescent protein tag to the intracellular mitochondrial network. Images were recorded in grayscale with a QImaging Retiga Fast-EXi camera system coupled to an Olympus BX-51 microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks provided by Omega Optical. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Additional Fluorescence Images of Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblast Cells
Indian Muntjac Cells with Enhanced Yellow Fluorescent Protein - A culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin cells was labeled with DAPI and Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin, which target DNA in the cell nucleus and the F-actin cytoskeletal network, respectively. In addition, the cells were transfected with a pEYFP-Mitochondria (enhanced yellow fluorescent protein) chimeric plasmid subcellular localization vector.
Peroxisomes in Muntjac Fibroblast Cells - The peroxisome organelles present in an Indian Muntjac fibroblast cell culture were immunofluorescently labeled with Rhodamine Red-X conjugated to antibodies directed against peroxisomal membrane protein 70 (PMP 70), an abundant and integral membrane component of peroxisomes. Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin and Hoechst 33258 were simultaneously used to counterstain the culture, targeting F-actin and DNA, respectively.
Indian Muntjac Skin Fibroblast Cellular Tubulin - The digital image appearing in this section features a resident cell from a culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblasts that was labeled for DNA with DAPI, and for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin. In addition, the culture was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Rhodamine Red-X.
Mitochondrial Distribution in Indian Muntjac Fibroblasts - An adherent culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblast cells was transfected with a pDsRed-Mitochondria plasmid subcellular localization vector, thus localizing a red fluorescent protein tag to the intracellular mitochondrial network. The culture was subsequently fixed and labeled with DAPI and Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, targeting DNA and filamentous actin, respectively.
Indian Muntjac Cells with Alexa Fluor 350, MitoTracker Red CMXRos, and SYTOX Green - In this section, the digital image features Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblast cells labeled for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin, and for the cell nucleus with SYTOX Green. Additionally, cellular mitochondria were stained with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, a complex aminated xanthene derivative.
Concanavalin A Localization in Indian Muntjac Fibroblasts - An adherent culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblasts was stained with Texas Red conjugated to the lectin concanavalin A, which selectively binds to alpha-mannopyranosyl and alpha-glucopyranosyl residues, primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum. Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin and DAPI were also used to counterstain the culture, targeting filamentous actin and nuclear DNA, respectively.
Muntjac Skin Fibroblast Cells with Alexa Fluor 568, Alexa Fluor 488, and DAPI - In a manner similar to the previous cell culture, the Indian Muntjac deer skin cells presented in this section were labeled with concanavalin A conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 to target the endoplasmic reticulum and selected carbohydrate residues found in glycoproteins, enzymes, and cell membranes. In addition, Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin was utilized to label the mitochondrial network, while DAPI was used to counterstain the nucleus.
Vinculin Distribution in Indian Muntjac Cells - Indian Muntjac fibroblast cells were immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-vinculin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab heavy and light chain fragments conjugated to Cy3 (red fluorescence emission). In addition, the specimen was simultaneously stained for DNA with the ultraviolet-absorbing probe Hoechst 33258, and for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin.
Visualizing Histones and the Golgi Complex in Monolayer Indian Muntjac Cell Cultures - The culture of Muntjac cells illustrated in this section was triple-labeled using double immunofluorescence and a phallotoxin. Nuclei were visualized with mouse anti-histones (core) primary antibodies, while the Golgi complex was stained with rabbit anti-giantin antibodies. Secondary antibodies were goat anti-mouse and anti-rabbit conjugated to Texas Red and Oregon Green 488, respectively to produce red nuclei and green Golgi cisternae. The filamentous actin network was counterstained with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin.
Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblast Cells with Alexa Fluor 568, Cy2, and DAPI - The Muntjac deer skin cells presented in this section were members of an adherent culture stained for F-actin with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin, and for DNA with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). In addition, the culture was immunofluorescently labeled with the cyanine fluorophore, Cy2, conjugated to goat secondary antibodies that target mouse anti-peroxisomal membrane protein 70 (PMP 70), a key membrane component of peroxisomes.
Indian Muntjac Cells with Alexa Fluor 488, DsRed Fluorescent Protein, and DAPI - A culture of Indian Muntjac fibroblast cells was transfected with a DsRed-Mitochondria plasmid subcellular localization vector to target cellular mitochondria. Stable transfectants were isolated and grown into log phase before being fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with DAPI and Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, targeting DNA in the cell nucleus and the F-actin cytoskeletal network, respectively.
Visualizing the Golgi Complex with Immunofluorescence in Indian Muntjac Fibroblast Cell Cultures - A log phase monolayer culture of Indian Muntjac cells was fixed, permeabilized, and blocked with 10-percent normal goat serum in phosphate-buffered saline prior to immunofluorescent labeling with rabbit primary antibodies to giantin, a protein resident in the Golgi complex of mammalian cells. The culture was subsequently stained with a mixture of goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody fragments (heavy and light chain) conjugated to Cy2. In addition, the culture was labeled for the filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin, and for DNA with Hoechst 33342.
Filamentous Actin, Mitochondria, and DNA Distribution in Indian Muntjac Fibroblasts - In this section, the digital image illustrates a culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblast cells labeled for filamentous actin with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin, and for the cellular mitochondrial network with MitoTracker Red CMXRos. SYTOX Green was also used to counterstain the cells, targeting nuclear DNA.
Adhesion Junctions in Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Cells - A culture of Indian Muntjac skin cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-vinculin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to the cyanine dye, Cy3. Vinculin is a protein associated with the cytoplasmic face of focal adhesions. In addition, the culture was counterstained for DNA with the probe Hoechst 33258, and for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin.
Intracellular Microtubules in Muntjac Fibroblasts - The expansive cellular microtubule network present in a culture of Indian Muntjac fibroblasts was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Rhodamine Red-X. The culture was also counterstained for DNA in the cell nucleus with Hoechst 33258.
Indian Muntjac Cells with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, Alexa Fluor 488, and DAPI - An adherent culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin cells was labeled with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, and DAPI, targeting mitochondria, F-actin, and nuclear DNA, respectively. Often used in combination, these fluorophores are very popular for multi-labeling experiments to ascertain distribution of subcellular components in fixed and permeabilized cell cultures.
Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblasts with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, Alexa Fluor 350, and SYTOX Green - In this section, the featured digital image illustrates a culture of Indian Muntjac cells labeled for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin, for intracellular mitochondria with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, and for DNA with SYTOX Green.
Indian Muntjac Cells with Enhanced Yellow Fluorescent Protein - A culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblast cells was transfected with a pEYFP-Mitochondria (enhanced yellow fluorescent protein) chimeric plasmid subcellular localization vector. After fixation and permeabilization, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin and DAPI, which target the F-actin cytoskeletal network and DNA in the cell nucleus, respectively.
Muntjac Fibroblasts with Alexa Fluor 488, MitoTracker Red CMXRos, and DAPI - Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblast cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin to target the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network, and for MitoTracker Red CMXRos to visualize the extensive intracellular tubular mitochondria. The cells were subsequently counterstained with DAPI, which targets DNA in the nucleus.
Targeting Peroxisomes in Indian Muntjac Fibroblast Cultures with Immunofluorescence - The peroxisomes present in the Indian Muntjac fibroblast cell culture featured in this section were immunofluorescently labeled with Cy2 conjugated to goat secondary antibody fragments directed against rabbit primary antibodies to peroxisomal membrane protein 70 (PMP 70), a major peroxisome membrane polypeptide. In addition, the culture was also labeled for F-actin with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin, and counterstained for nuclear DNA with DAPI.
Actin, Mitochondria, and DNA Localization in Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Cells - An Indian Muntjac fibroblast cell culture was labeled with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin, targeting the F-actin cytoskeletal network. The cells were also stained with MitoTracker Red CMXRos and SYTOX Green, which preferentially bind with intracellular mitochondria and DNA in the cell nucleus, respectively.
Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblast Cell Cultures with Cy2, Alexa Fluor 568, and DAPI - The digital image presented in this section features a culture of Indian Muntjac fibroblast cells that was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to the cyanine dye, Cy2. In addition, the culture was counterstained for DNA with DAPI, and for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin.
The Golgi Apparatus in Indian Muntjac Cells - A culture of Indian Muntjac fibroblasts was fixed, permeabilized, and blocked with 10-percent normal goat serum in phosphate-buffered saline prior to immunofluorescent labeling with primary antibodies to giantin, a protein resident in the Golgi complex of mammalian cells. The culture was subsequently stained with secondary antibody fragments (heavy and light chain) conjugated to Cy2. In addition, the culture was labeled for mitochondria with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, and for DNA with Hoechst 33342.
Targeting the Mitochondria Network with Fluorescent Proteins in Indian Muntjac Cells - In a manner similar to several specimens linked above, an adherent culture of Indian Muntjac deer skin fibroblast cells was transfected with a pDsRed-Mitochondria plasmid subcellular localization vector, thus localizing a red fluorescent protein tag to the intracellular mitochondrial network. The culture was subsequently fixed and labeled with Hoechst 33342 and Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, targeting DNA and filamentous actin, respectively.
Histone and Peroxisome Distribution in Indian Muntjac Cell Cultures - In a double immunofluorescence experiment, an adherent monolayer culture of Indian Muntjac cells was fixed, permeabilized, blocked with 10 percent normal goat serum, and treated with a cocktail of mouse anti-histones (pan) and rabbit anti-PMP 70 (peroxisomal membrane protein) primary antibodies, followed by goat anti-mouse and anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Texas Red and Oregon Green 488, respectively. The filamentous actin network was counterstained with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin.
Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblast Cells with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, BODIPY FL, and Hoechst 33258 - The popular triple fluorophore combination of MitoTracker Red CMXRos, BODIPY FL conjugated to phalloidin, and Hoechst 33258 was used to label an adherent log phase culture of Indian Muntjac cells for mitochondria, the filamentous actin network, and nuclear DNA. The cells were first treated with MitoTracker Red CMXRos in growth medium for one hour, washed and fixed with paraformaldehyde (prepared in growth medium), permeabilized, and blocked with bovine serum albumen. The cells were subsequently labeled with the conjugated phalloidin and counterstained with the bisbenzimide reagent.
BACK TO THE CULTURED CELLS FLUORESCENCE GALLERY
BACK TO THE FLUORESCENCE GALLERY
