Fluorescence Digital Image Gallery
Male Rat Kangaroo Kidney Epithelial Cells (PtK2)
The widely used PtK2 cell line was established from the kidney tissue of an adult male rat kangaroo (Potorous tridactylus), a long-nosed, marsupial that is fairly common in Australia. The epithelial line is positive for the tough, insoluble intermediate filament protein keratin by immunoperoxidase staining, but is negative for reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes.
PtK2 cells are susceptible to coxsackievirus A9, herpes simplex, vaccinia, and vesicular stomatitis (Ogden strain). The cells are resistant, however, to adenovirus 5, coxsackievirus B5, and poliovirus 2. The PtK2 epithelial cell line is utilized for a variety of applications, but primarily for research in the field of mitosis.
Mitosis is a phenomenon observed in all higher eukaryotes that allows the nuclei of cells to split and provide each daughter cell with a complete set of chromosomes during cellular division. Living PtK2 cells grown in culture are often used to visualize mitosis in the microscope because they contain a relatively small number of large chromosomes. Moreover, PtK2 cells tend to remain relatively flat throughout the mitotic process, making it even simpler to observe all of the division stages. At 37 degrees Celsius, the marsupial epithelial cells undergo mitosis in approximately 2 to 3.5 hours. A typical healthy, growing PtK2 culture often contains many cells at every stage of the mitotic process.
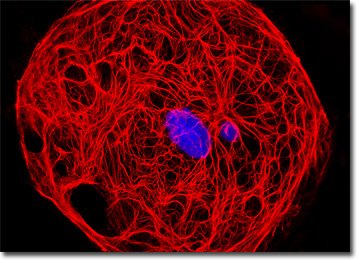
The male rat kangaroo kidney cell that appears in the digital image presented above was resident in a culture immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-cytokeratin (pan) mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Cy3. In addition, DAPI was used to counterstain DNA present in the nucleus. Images were recorded in grayscale with a QImaging Retiga Fast-EXi camera system coupled to an Olympus BX-51 microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks provided by Omega Optical. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Additional Fluorescence Images of Male Rat Kangaroo Kidney (PtK2) Cells
PtK2 Cells with Marina Blue and MitoTracker Red CMXRos - The adherent rat kangaroo kidney cell culture presented in this section was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-cytokeratin (pan) mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Marina Blue. The specimen was simultaneously stained with MitoTracker Red CMXRos to label the mitochondrial network.
Beta-Catenin Linking Proteins in PtK2 Cells - A culture of rat kangaroo kidney cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-beta-catenin rabbit monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody fragments (Fab) conjugated to Rhodamine Red-X. Members of the catenin family of peripheral cytosolic proteins bind selectively to the highly conserved cytoplasmic tail domain of the cell-to-cell adhesion cadherin proteins. In addition, the specimen was subsequently counterstained for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, and for DNA in the cell nucleus with Hoechst 33258.
Rat Kangaroo Kidney Epithelial Cells with Texas Red, Alexa Fluor 488, and DAPI - In this section, the PtK2 cells presented were resident in a culture fluorescently labeled with Texas Red conjugated to the enzyme DNase I, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, and DAPI, targeting globular (unpolymerized) actin, the filamentous F-actin network, and nuclei, respectively.
The Microtubule Network and Nuclear DNA in PtK2 Cells - A culture of male rat kangaroo kidney (PtK2 line) cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Cy2. In addition, the cells were counterstained for DNA with the ultraviolet-absorbing probe, DAPI.
Rat Kangaroo Kidney Cellular Tubulin Network - In a manner similar to the previous culture, the extensive microtubular network present in PtK2 cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Cy3. The epithelial cells were also stained with DAPI, which preferentially binds to nuclear DNA.
Cytokeratin in PtK2 Epithelial Cells - An adherent culture of male rat kangaroo kidney epithelial cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-cytokeratin (pan) mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to the cyanine probe, Cy2. In addition, the cells were counterstained with MitoTracker Red CMXRos and DAPI, targeting the mitochondrial network and DNA, respectively.
Intermediate Filaments in Rat Kangaroo Kidney Cells - In this section, the featured culture of rat kangaroo kidney epithelial (PtK2) cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-vimentin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Rhodamine Red-X. Vimentin is a protein present in the intermediate filaments of many cell lines derived from the mesoderm. The cell culture was also counterstained for DNA with DAPI.
G-Actin, F-Actin, and DNA in PtK2 Cells - The single rat kangaroo kidney epithelial cell that appears in the digital image presented in this section was resident in a culture fluorescently labeled with Texas Red conjugated to the enzyme DNase I, targeting globular (unpolymerized) actin. The specimen was also labeled for filamentous actin with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, and for nuclear DNA with DAPI.
Immunofluorescence Labeling of Beta-Catenin and Tubulin in Rat Kangaroo Kidney Cells - The technique of double immunofluorescence was employed to simultaneously label an adherent culture of rat kangaroo kidney cells with mouse anti-tubulin and rabbit anti-beta-catenin primary antibodies, followed by goat anti-mouse and anti-rabbit secondary antibodies conjugated to Marina Blue (tubulin) and Rhodamine Red-X (beta-catenin), respectively. The culture was counterstained with SYTOX Green, targeting the DNA present in the cell nucleus.
PtK2 Cells with Fluorescein, MitoTracker Red CMXRos, and DAPI - An adherent culture of PtK2 epithelial cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-cytokeratin (pan) mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to fluorescein. In addition, the specimen was stained with MitoTracker Red CMXRos and the ultraviolet-absorbing probe DAPI, which bind with mitochondria and DNA, respectively.
Beta-Catenin Proteins and Microtubules in PtK2 Kidney Cells - In this section, the featured digital image presents a culture of male rat kangaroo kidney epithelial cells that was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-beta-catenin rabbit monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies conjugated to Rhodamine Red-X. The culture was also immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Cy2 to target the microtubular network, and counterstained with Hoechst 33342 to target nuclear DNA.
PtK2 Epithelial Cells with Cy2 and DAPI - An adherent culture of male rat kidney kangaroo (PtK2 line) cells was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Cy2. In addition, the cells were stained with DAPI, which binds to DNA in the cell nucleus.
Distribution of Vimentin and Filamentous Actin in Adherent Rat Kangaroo Kidney Epithelial Cell Cultures - In order to label the intermediate filaments in a log phase adherent PtK2 culture, the fixed and permeabilized cells were blocked and treated with mouse anti-vimentin (porcine eye lens) primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Texas Red-X. Filamentous actin was visualized with phalloidin conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488, while the nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258.
BACK TO THE CULTURED CELLS FLUORESCENCE GALLERY
BACK TO THE FLUORESCENCE GALLERY
