Fluorescence Digital Image Gallery
Human Fetal Lung Fibroblast Cells (MRC-5 Line)
The MRC-5 cell line is commonly utilized in vaccine development, as a transfection host in virology research, and for in vitro cytotoxicity testing. Initiated in September 1966 by J. P. Jacobs, the cell line was derived from the human lung tissue of a 14-week-old male fetus aborted from a 27-year-old woman.
MRC-5 cells, which grow adherently in culture and exhibit fibroblast morphology, may double in population size 42 to 46 times before the onset of senescence. They are susceptible to poliovirus 1, herpes simplex, and vesicular stomatitis (Indiana strain). The line is, however, negative for reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes.
Since the development of an increased awareness of terrorist threats to the United States, the MRC-5 cell line has come under more significant attention due to its role in the preparation of smallpox vaccines. Vaccinations for smallpox have not been required in the country since the early 1970s because the disease was almost completely eliminated from the United States. However, smallpox, which is caused by a virus known as Variola major, is now considered an extremely dangerous potential biological weapon because it is readily transmitted from person to person and few individuals are fully immune to it. Smallpox vaccines have been shown to be highly effective in preventing infection and in decreasing the severity of illness to those that were exposed without protection. Thus, an attempt is being made to ensure that enough vaccines are available for all inhabitants in case an outbreak occurs. Many of the new vaccines are being produced utilizing the MRC-5 cell line rather than the calf skin cells that served as the basis for many of the older smallpox vaccines.
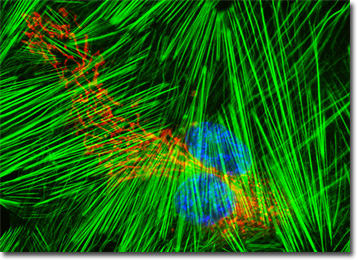
The culture of human fetal lung fibroblast (MRC-5) cells presented in the digital image above was labeled with wheat germ agglutinin, a lectin that targets glycoproteins in the Golgi network, conjugated to Texas Red-X. In addition, the cells were labeled for the cytoskeletal F-actin network and DNA with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin and DAPI, respectively. Images were recorded in grayscale with a QImaging Retiga Fast-EXi camera system coupled to an Olympus BX-51 microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks provided by Omega Optical. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Additional Fluorescence Images of Human Fetal Lung Fibroblast (MRC-5) Cells
MRC-5 Cells with Cy3, Alexa Fluor 488, and Hoechst 33258 - A culture of human lung fetal fibroblast cells was stained with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, which targets cytoskeletal filamentous actin, and Hoechst 33258, which binds to DNA in cell nuclei. The MRC-5 cells were also immunofluorescently labeled with anti-tubulin mouse monoclonal primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to Cy3, targeting the intracellular microtubular network.
Visualizing Structural Features of the Golgi Complex and Nucleus in Human Lung Fibroblast Cells - In order to examine structural features of the Golgi complex and nucleus at relatively high magnification, a log-phase culture of MRC-5 cells was fixed, permeabilized, blocked with normal goat serum, and then treated with rabbit anti-giantin (Golgi protein) primary antibodies followed by goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568. The nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258.
Mitochondrial Distribution in Fetal Lung Fibroblasts - The mitochondria present in the culture of MRC-5 fibroblasts featured in this section were targeted with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, a derivative of X-rosamine. In addition, the culture was labeled for nuclear DNA and the cytoskeletal F-actin network with the ultraviolet-absorbing probe DAPI and Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, respectively.
The Filamentous Actin Network in MRC-5 Fibroblast Cells - In this section, the single human fetal lung fibroblast (MRC-5) cell that is featured was resident in a culture that was stained with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin, which binds to the intracellular filamentous actin network. The cells were subsequently stained with Hoechst 33258 (targeting DNA in the cell nucleus) and the lectin wheat germ agglutinin conjugated to Oregon Green 488 (targeting glycoproteins in the Golgi complex).
Histone and Peroxisome Distribution in Human Fetal Lung Cell Cultures - In a double immunofluorescence experiment, an adherent monolayer culture of MRC-5 cells was fixed, permeabilized, blocked with 10 percent normal goat serum, and treated with a cocktail of mouse anti-histones (pan) and rabbit anti-PMP 70 (peroxisomal membrane protein) primary antibodies, followed by goat anti-mouse and anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Texas Red and Alexa Fluor 488, respectively. The filamentous actin network was counterstained with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin.
Concanavalin A Localization of the Endoplasmic Reticulum in MRC-5 Monolayer Cell Cultures - A culture of human fetal lung fibroblast cells was stained with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to the lectin concanavalin A, which selectively binds to alpha-mannopyranosyl and alpha-glucopyranosyl residues (primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum). Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin and SYTOX Green were also used to label the culture, targeting filamentous actin and nuclear DNA, respectively.
Human Lung Fibroblast Cells with Texas Red-X, Oregon Green 488, and Hoechst 33258 - In order to label the intermediate filaments in a log phase adherent MRC-5 culture, the fixed and permeabilized cells were blocked and treated with mouse anti-vimentin (porcine eye lens) primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Texas Red-X. Filamentous actin was visualized with phalloidin conjugated to Oregon Green 488, while the nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258.
BACK TO THE CULTURED CELLS FLUORESCENCE GALLERY
BACK TO THE FLUORESCENCE GALLERY
