Polarized Light Microscopy Digital Image Gallery
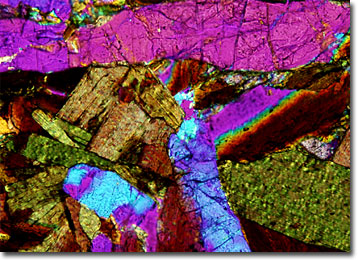
Sodalite Syenite
Syenite was originally a designation utilized to refer to rocks that were similar to a hornblende granite found in Syene, Egypt. The term was coined by Pliny the Elder, author of Natural History, a comprehensive work that served as cornerstone of scientific knowledge until the Middle Ages.
View a second image of Sodalite Syenite
In modern times, syenite is generally defined as a type of intrusive igneous rock that is coarse-grained and similar in composition to granite. However, quartz is usually absent or only present in very small amounts in syenite. Most syenites are basically comprised of an alkali feldspar, such as orthoclase, albite, perthite, or microcline, and a ferromagnesian mineral. Commonly this mineral will be hornblende, but biotite and pyroxene occur frequently in the rocks as well.
Syenites are often named based upon the chief ferromagnesian mineral they contain. Thus, sodalite syenite is a type of syenite that contains appreciable amounts of sodalite, a sodium aluminosilicate mineral. This variety of rock may also include a wide array of other minerals, such as granconite, rutile, pyrite, and gypsum, but in smaller amounts. Relatively rare, sodalite syenite is typically lighter in color than more common varieties of the rock, generally exhibiting a pale gray to beige hue.
