Kodak Color Compensating Filters
Green CC Filter Series
Kodak color compensating filters are frequently used to fine-tune the color balance of tungsten-halogen microscope light sources for photomicrography with color films. These gelatin filters control color by absorbing different amounts of the red, green and blue parts of the visible light spectrum.
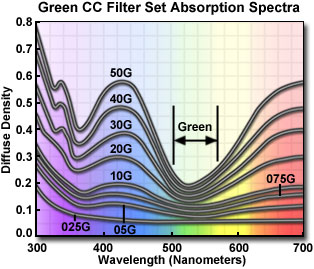
The visible absorption spectra for a set of green color compensating filters are illustrated above. These filters have principal absorption maxima at 340 (ultraviolet), 430 (blue) and 700 (red) nanometers, and display minimum absorption in the green (500-570 nanometers) visible light region.
Color compensating filters are labeled with a number to indicate their ability to absorb light. The most common densities are 05, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50, in which larger numbers denote denser (darker) filters. A typical filter designation code is given as:
where
CC = Color Compensating filter50 = filter nominal peak density
G = filter color (Green)
Nominal peak densities of green color compensating filters are listed in Table 1, along with the expected exposure increase in f-stops for this series of filters.
Green Filter Factors
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1
Transmittance data as a function of wavelength is listed in Table 2 for the most common green color correction filter nominal peak densities.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2
The blue region of the spectrum is between 400 and 500 nanometers. The green region is between 500 and 600 nanometers, and the red region is between 600 and 700 nanometers.
Determining the density of a color compensating filter first requires measuring the filter's density with respect to its complimentary color. For example, a red color compensating filter has a low density to red light but a higher density to blue and green light (which combine to form cyan, the complimentary color of red). To determine the density, measure the density of the filter to its own color of light (red light to a CC Red filter). In this example let us assume that red = 0.02. Next, measure the filter density to blue and green light (again, in this example assume green = 0.07 and blue = 0.08). The average of the green and blue readings is:
After the neutral density (filter's density to color of its own light) has been subtracted:
The remainder is 0.055, which is very close to the 0.05 value indicated for the CC05R filter.
Contributing Authors
Mortimer Abramowitz - Olympus America, Inc., Two Corporate Center Drive., Melville, New York, 11747.
Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.
