Wim van Egmond
Micrasterias thomasiana
Unable to be seen by the naked eye, the microscope has the power to reveal the beauty of the unicellular green algae known as desmids. These tiny organisms exhibit tremendous variability in their cell shape and ornamentation, making them an extremely interesting group to study.
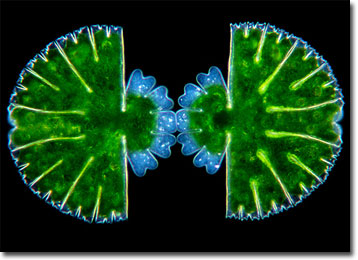
Micrasterias is a genus whose members are considered placoderm desmids, those that feature a cell wall composed of two sections that attach in the mid-region. This type of desmid is also characteristically furnished with pores, spines, granules, or other protuberances. Contrariwise, saccoderm desmids typically possess a smooth, unornamented cell wall that consists of a single piece. As placoderm desmids, the more than 40 known species of Micrasterias exhibit a substantial amount of diversity in the adornment of their lobed, disclike shapes, and many are among the most picturesque microscopic life forms in the world. Most often found in acidic waters and bogs, the organisms may grow between 80 to 200 micrometers in diameter.
Micrasterias thomasiana is one of the commoner species of its genus. The approximately circular cells are characterized as being large and flat with a deep incision near the median, which divides each organism into two semicells. The semicells are divided into a polar lobe and two lateral lobes that sometimes are divided again. Micrasterias thomasiana has often been utilized in research and multiplies primarily through asexual means. When this occurs, the cells divide at the nucleus located in the central isthmus and each half produces a new semicell. Thus, each half of the resulting desmid is a different age, and one semicell may be significantly smaller than the other until sufficient growing time has elapsed.
BACK TO WIM VAN EGMOND GALLERY
