Eastern Cottonwood
The Eastern Cottonwood (Populus deltoides; sometimes referred to as the Eastern Poplar) is a hardwood tree most commonly found in the eastern United States in the Great Plains, but it is not common in most of the northeast or the Appalachians. The tree averages 80 to 100 feet in height and has a deeply fissured bark and very broad crown. The sapwood is whitish and frequently merges into the heartwood (ranging from grayish white to light gray-brown in color), making it difficult to clearly define.
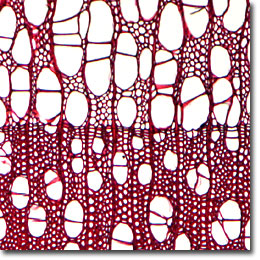
Cross Section

Radial Section

Tangential Section
According to the Indian legend, the original design for a teepee was discovered by a brave who twisted a cottonwood leaf around his fingers, forming a miniature teepee. Pulp from this wood is often used to make high-grade book and magazine paper. The Eastern cottonwood is widely used as a veneer for the manufacture of plywood, furniture, and musical instrument containers. Lumber is used for pallets, boxes, crates, and is very well known for ease of nailing without splitting.
Microscopic examination of iron-alum hematoxylin and safranin stained thin sections (see the digital images presented above) reveals a diffuse and porous wood having simple perforation plates. The vessels are medium in size and relatively numerous, with inter-vessel pits ranging from 9 to 13 micrometers in diameter and having an orbicular to oval or angular (through crowding) shape. Parenchyma is marginal and forms a narrow, terminal line. Libriform fibers are coarse to very coarse in texture, are occasionally gelatinous, and thick-walled. The rays are uniseriate, unstoried, and essentially homocellular.