AMD Integrated Circuits
Athlon Microprocessor
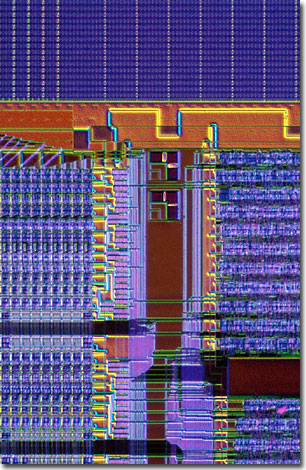
With subtle blue and yellow oblique highlights, a memory cache and part of the floating point unit on the surface of the AMD Athlon microprocessor appear in relief when imaged in differential interference contrast (DIC) using a reflected light microscope. Note the twin mask alignment targets in the left-hand center of the digital image presented below.
Examine a larger version of this digital image.
The first member of AMD's seventh-generation family of microprocessors, the Athlon was designed for desktop computers, workstations, and servers. The processor's high-speed execution core includes multiple x86 instruction decoders, a dual-ported 128-kilobyte level one (L1) cache, and three independent integer pipelines. In addition, the floating point engine is capable of delivering 2.4 gigaflops of single-precision calculations and more than a gigaflop of double-precision floating point results when the chip is operated at 600 megahertz.
BACK TO AMD INTEGRATED CIRCUITS