Polarized Light Digital Image Gallery
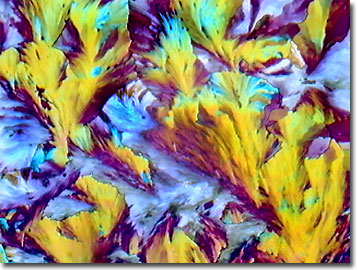
Niacin (Vitamin B-3)
Niacin (vitamin B-3), more commonly known as nicotinamide in the biochemical community, plays an important role in the biosynthesis of pyridine nucleotides. This nitrogen heterocyclic organic compound is combined in vivo with the nucleotide adenosine to form nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
View a second image of niacin.
Natural sources of niacin include cheese, beans, milk, meat, poultry, fish, eggs, whole grains, and brewer's yeast. Clinically, niacin helps maintain normal function of the digestive system, helps reduce cholesterol levels, and helps eliminate dizziness and ringing in the ears. Known also as nicotinic acid, 3-carboxypyridine, or 3-pyridinecarboxylic acid, vitamin B-3 features 6 carbons, 5 hydrogens, 1 nitrogen, and 2 oxygen atoms per molecule with a molecular weight of 123.11. Available also as a synthesized white crystalline powder or as white crystals, niacin is slightly soluble in water and has a melting point of 237 degrees Celsius.
As a natural peripheral vasodilator, niacin is used topically and orally to promote hair growth. The United States Food and Drug Administration sets the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin B-3 as 19 milligrams for men and 15 milligrams for women. In the body, the amino acid tryptophan can be biosynthesized into niacin, making vitamin B-3 one of the non-essential vitamins. Reportedly, niacin is involved in more than 50 different enzymatic reactions, aids in the formation of red blood cells, and is considered essential for healthy skin, tongue, and digestive tract tissues. Many hormones, such as cortisone, the sex hormones, and insulin, depend on niacin for their synthesis.
Absorbed in the small intestine, niacin is excreted in the urine although a small amount may be stored in the liver. Severe deficiency in vitamin B-3 is recognized by the skin disease pellagra as well as diarrhea, lethargy, a sore tongue and mouth, dementia, and depression. Originally observed in cultures whose diets relied heavily on corn (no available niacin), large amounts of dietary tryptophan can overcome a niacin poor diet. Often alcoholics and the elderly suffer from niacin shortfalls as do some patients on an antibiotics regime.
Contributing Authors
Omar Alvarado, Thomas J. Fellers and Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.
BACK TO THE POLARIZED LIGHT IMAGE GALLERY
BACK TO THE DIGITAL IMAGE GALLERIES
Questions or comments? Send us an email.
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
Graphics & Web Programming Team
in collaboration with Optical Microscopy at the
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory.
Last Modification Friday, Nov 13, 2015 at 01:19 PM
Access Count Since September 17, 2002: 14196
Visit the website of our partner in introductory microscopy education:
|
|
