Oblique Digital Image Gallery
Water Flea (Daphnia)
Water fleas (more commonly known as Daphnia) are microscopic crustaceans, belonging to the order Cladocera, that populate the quiet waters of lakes and ponds throughout the world. Most species are found in freshwater habitats, but a few occur in marine environments. Daphnia has a discrete head bearing antennae and a bivalve carapace that encloses all or most of the trunk and abdomen.
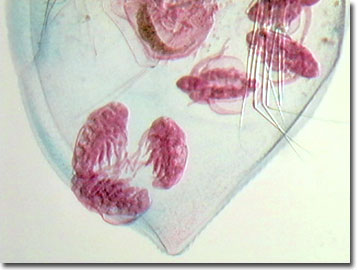
While it is barely visible to the naked eye, under the microscope the creature's internal structures can be easily discerned, particularly the beating heart that lies along the back. Daphnia is one of many groups of cladocerans nicknamed "water fleas" because of their resemblance to the common flea and their characteristic "hopping" locomotion associated with the strongly beating antennae.
Like other cladocerans, daphnia are an important part of the food chain, filter-feeding on microscopic particles and phytoplankton and, in turn, providing food for juvenile fish. In the Great Lakes of North America, water fleas are the basic food for nearly all commercial fish species.
Cladocerans, such as Daphnia, are parthenogenetic most of the year, producing unfertilized eggs that, in turn, produce females. Towards the end of seasonal population peaks, in a mechanism not well understood, parthenogenetic females produce parthenogenetic male eggs. Sexual females are also produced parthenogenetically. They copulate with the males, producing a small number of resistant eggs. These resistant eggs can overwinter, withstand drying and freezing, etc. and will hatch when conditions permit. The eggs aid in dispersal between bodies of water and allow species to endure in ephemeral habitats.
Contributing Authors
Cynthia D. Kelly, Thomas J. Fellers and Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.
BACK TO THE OBLIQUE IMAGE GALLERY
BACK TO THE DIGITAL IMAGE GALLERIES
Questions or comments? Send us an email.
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
Graphics & Web Programming Team
in collaboration with Optical Microscopy at the
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory.
Last Modification Friday, Nov 13, 2015 at 01:19 PM
Access Count Since September 17, 2002: 14652
Visit the website of our partner in introductory microscopy education:
|
|
