Advanced Condenser Systems: Abbe Condensers
Hadrosaurus Bone
The digital images presented below were recorded with a QX3 microscope body and an Abbe substage condenser equipped for transmitted Rheinberg illumination. These photomicrographs are unretouched and were captured with the QX3 interactive software.
Hadrosaurus Bone
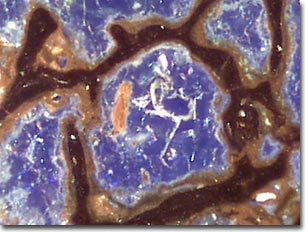
(Blue Central and Red/Yellow Annular Gels)
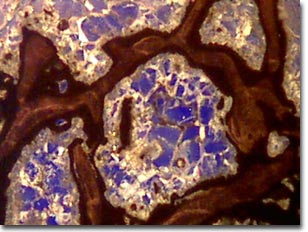
with Abbe Condenser
(Blue Central and Red/Yellow Annular Gels)
The hadrosaurs, often referred to as the "duckbilled dinosaurs", were a group of plant-eating dinosaurs that evolved during the Jurassic era, 135-205 million years ago. By the end of the Cretaceous era, 65 million years ago, they were widely distributed in Europe, Asia, and North America.
Some species of hadrosaurs had large crests, the function of which has baffled scientists for many years. Curiously, the nasal passages loop from the nose through the crest, forming large sinuses (spaces in the skull) before passing into the airway. Today, the most accepted theory of the crest's function is that it served as a resonating chamber, allowing these dinosaurs to call to each other with warnings of predators or to attract potential mates. The crest may also have functioned as a visual display device to attract mates.
Hadrosaurs were fairly large, ranging in length from 27 to 33 feet (9-11 meters). Fossil evidence shows that they had webbed hands, suggesting that they spent at least part of their lives in bodies of water. However, their stiff tails, supported by ossified tendons, as well as their sturdy bones and rapidly-replaced teeth, indicate that hadrosaurs spent most of their time on land feeding on tough terrestrial plants. Discoveries of spectacularly preserved hadrosaur nests with eggs and young shows that hadrosaurs migrated to higher ground to reproduce.
Semi-transparent specimens are difficult to image using unaided brightfield optical microscopy. The images above were recorded using the Intel Play QX3 microscope in transmitted brightfield mode with the assistance of Rheinberg illumination. Dyed acetate gel filters were strategically placed below the aperture diaphragm of an aftermarket Abbe-style condenser to generate the Rheinberg effect. A 15-millimeter central filter was surrounded by a larger annular filter to combine the effects of oblique specimen illumination by light filtered through the annular filter superimposed over a background of light filtered through the central filter.
BACK TO INTEL QX3 ADVANCED RHEINBERG GALLERY
