Fluorescence Digital Image Gallery
Human Bone Osteosarcoma Cells (U-2 OS)
|
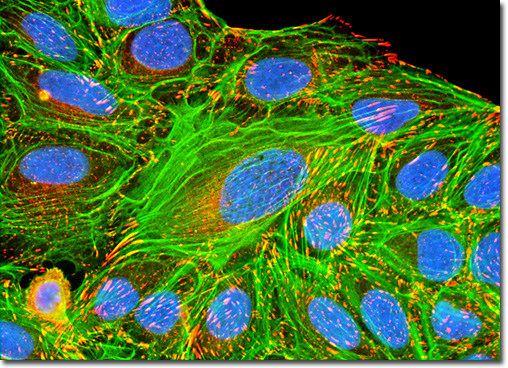
The production of antibodies in vitro was introduced by Georges K÷hler and CÚsar Milstein, who first employed cultures of fused cells to isolate antibodies of defined specificity. In this procedure, termed monoclonal antibody production, antibodies are first produced in mice, and activated B-lymphocytes from the host's spleen (the source of antibodies) are fused with cultured plasma tumor myeloma cells (that do not produce antibodies) from mice of the same strain. The fusion product is a hybrid (termed a hybridoma) of the two cells that continues to grow and divide in culture and produces large amounts of the antibody. Unfused cells and non-productive fusions are eliminated by classical cloning techniques to purify the culture of antibody-producing cells. A hybrid cell line produces only a single type of antibody, which can be used as a selection marker in serial dilution cloning by monitoring the culture medium for secreted antibody at each stage. Ultimately a cell line is established from a single cell (monoclonal) in which all of the cells produce an identical antibody. The culture of human osteosarcoma cells featured above was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-vinculin mouse monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab heavy and light chain fragments conjugated to Cy3. Vinculin is a protein associated with focal adhesion and adherens junctions, which are membrane-associated complexes that serve as nucleation sites for actin filaments and as crosslinkers between the external medium, plasma membrane, and actin cytoskeleton. The cells were also stained with the DNA-specific fluorophore DAPI and an Alexa Fluor 488 phalloidin conjugate in order to target cytoskeletal F-actin. Images were recorded in grayscale with a QImaging Retiga Fast-EXi camera system coupled to an Olympus BX-51 microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks provided by Omega Optical. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|