|
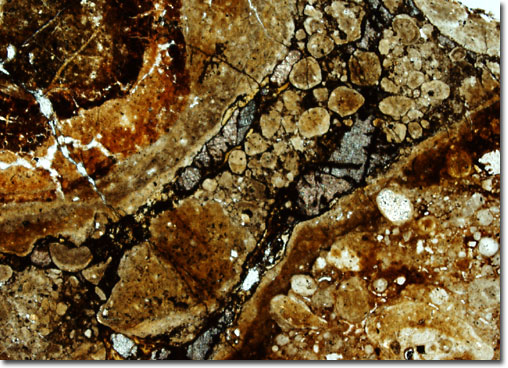
Generally formed though the weathering of a variety of rocks, in addition to hydrous aluminum oxides, bauxite may contain quartz, kaolinite, magnetite, hematite, rutile, zircon, and a number of other minerals. Due to their wide array of possible compositions, as well as to differences in geologic history, bauxites vary significantly in structure and hue. They may, for instance, be hard or soft, porous or dense, stratified or mottled, and gray, brown, yellow, red, or pink in color. Most deposits of bauxite, however, do occur near the surface of the Earth, where they can be readily obtained through open-pit mining methods.
|