Fluorescence Digital Image Gallery
Embryonic Swiss Mouse Fibroblast Cells (3T3)
|
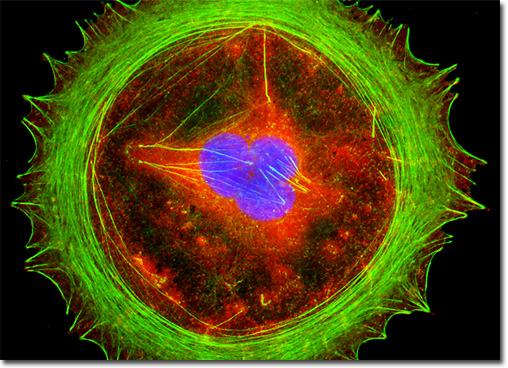
Catenins belong to a class of intracellular linking agents that serve to bind the highly conserved cytoplasmic tail domain of several cadherin transmembrane adhesion proteins to the actin cytoskeleton. There are three distinct peripheral cytoplasmic catenin proteins, termed alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin, which may be involved in mediating transduction of intercellular contact positional signals to the cell interior. Beta-catenin binds directly to the cytoplasmic tail of E-cadherin, as well as to the N-terminal region of alpha-catenin in a complex that includes a tumor suppressor gene product, known as adenomatous polyposis coli (APC). The intracellular levels of beta-catenin appear to be controlled, at least in part, by the suppressor protein. The single log phase Swiss mouse embryo cell presented above was resident in a culture that was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-beta-catenin rabbit monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies conjugated to Rhodamine Red. In addition, nuclear histone proteins were targeted with anti-histone (pan) monoclonal antibodies, which were imaged with goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) conjugated to Marina Blue (labeling the nucleus). The specimen was subsequently counterstained for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin. Images were recorded in grayscale with a QImaging Retiga Fast-EXi camera system coupled to an Olympus BX-51 microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks provided by Omega Optical. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|