|
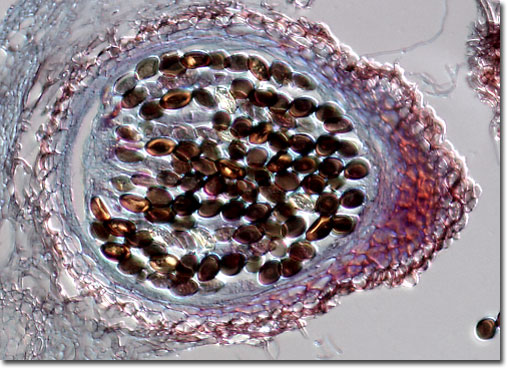
The popularity of using S. fimicola as an instructional tool is largely due to its simplicity with which to work. The fungus grows well in culture and can produce mature perithecia, or fruiting bodies, in about a week. Students can then easily observe the meiotic division of the diploid perithecia, which produce ordered linear tetrads encased in the ascus sac. Subsequently, these tetrads are converted to octads by mitosis of the haploid ascospores, providing students with the opportunity to learn about another important biological process.
|