Brightfield Microscopy Digital Image Gallery
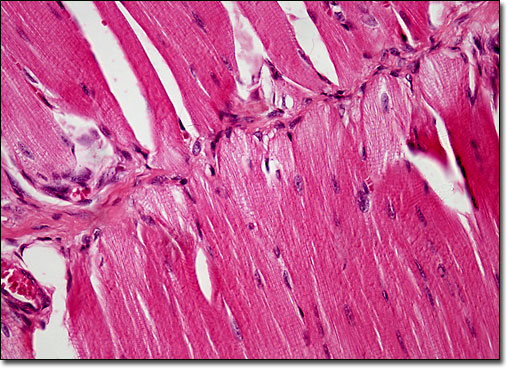
Mammalian Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
Comprised of elongated cells with multiple nuclei, cardiac muscle tissue appears striated under the microscope. Yet, unlike other striated muscles in the body, cardiac muscle controls an involuntary action, similar to smooth muscle tissue. The rhythmically contracting cardiac muscle tissue is essentially under the control of the heartís pacemaker, the sinoatrial node. However, a number of chemical substances may affect the action of the tissue, many of which are utilized for medical purposes. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|