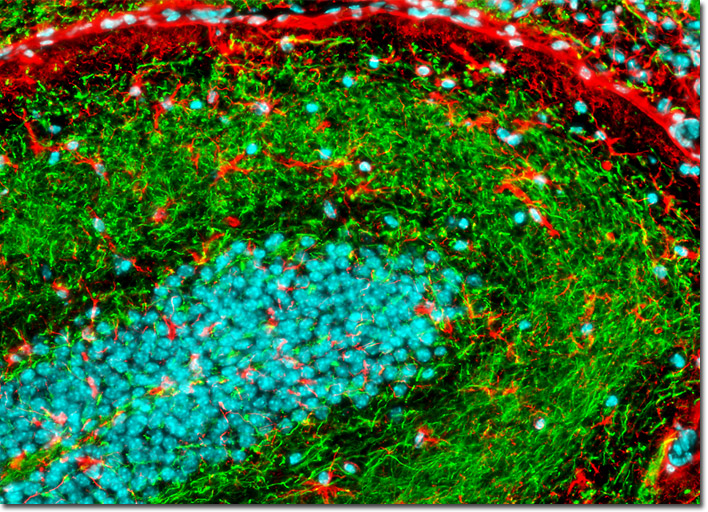
Mouse Brain Post Hypothalamus Region
|
The hypothalamus is associated with the rhythmic behaviors of the body, especially the daily rhythms known as circadian rhythms. The suprachiasmatic nuclei located in the hypothalamus are thought to serve as one of the body's primary biological clocks, and the paired structures are linked to the pineal gland so that they function in the regulation of melatonin secretion. The hypothalamus also interacts with the pituitary gland and heavily influences its activity, including the release of growth hormone and luteinizing hormone, among others. Weight, body heat, hunger, thirst, fluid intake, pleasure, and mating behavior are some of the many other properties and activities heavily impacted by the hypothalamus. View a smaller version of this image. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|