|
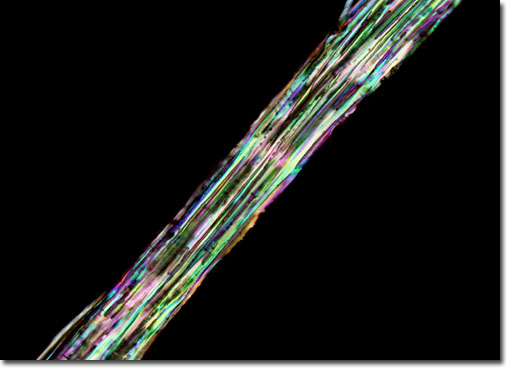
A relative of cotton and okra, kenaf grows at a rapid pace, attaining heights as great as 14 feet in a single season. The stems of the plant are comprised of two different fibers, both of which are exploited commercially. An inner fiber, commonly referred to as the core, is woody, exhibiting coarseness and other properties similar to the fibers of hardwood trees. This material is heavily utilized in a wide array of paper products, as well as in particleboard. The fiber described as bast, however, is much softer and more flexible than the core it surrounds, making it a better-suited and more popular choice for many textiles and cordages.
|