|
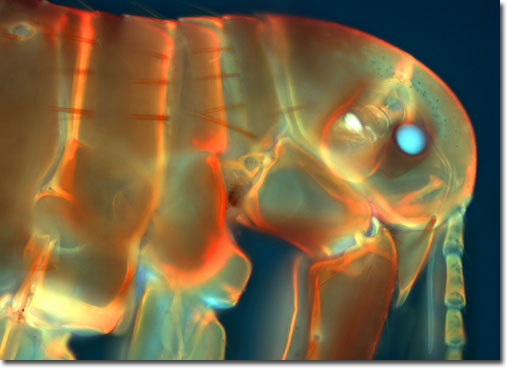
The human flea is not the primary species responsible for transmitting the bubonic plague throughout Europe during the Middle Ages (that dubious honor belongs to the rodent flea), although it is capable of spreading it. One disease that Pulex is known to transmit, however, is murine typhus, a mild form of typhus caused by the bacterium Rickettsia prowazekii. The flea becomes infected by feeding on a human who has the disease and the bacteria grows in the epithelial cells lining the flea's gut wall, eventually being excreted in the insect's feces. The infection kills the flea after 12 to 18 days. A person becomes infected by scratching the flea bite, thus rubbing the flea's infected feces into the wound. After an incubation period of one to two weeks, an infected person experiences headaches, loss of appetite, malaise, and a rapid rise in temperature with fever, chills, marked prostration, and nausea. Four to six days later a rash appears over most of the body.
|