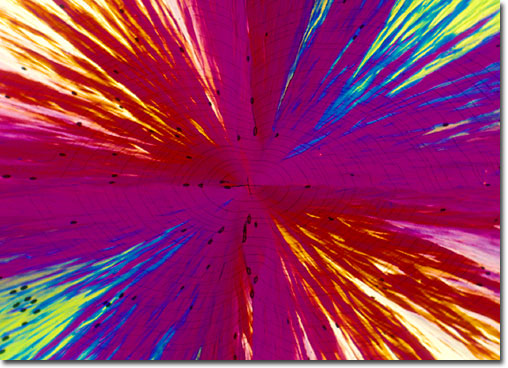
Monuron
View a second image of monuron.
|
This herbicide is a member of the substituted urea class of pesticides, which are relatively nonselective and are usually applied to the soil as pre-emergence herbicides. However, some substituted ureas have post-emergence uses, while others are active when foliar applied. The ureas are readily absorbed by the roots and rapidly translocated to the upper plant segments, producing phytotoxic symptoms that are most visible in the leaves. The primary site for biological activity appears to the Hill photosynthetic reaction, although other mechanisms have been postulated. Monuron has been used for pre-emergence control of broad-leaved and grass weeds to protect crops such as cotton, sugarcane, pineapple, asparagus, and citrus. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|