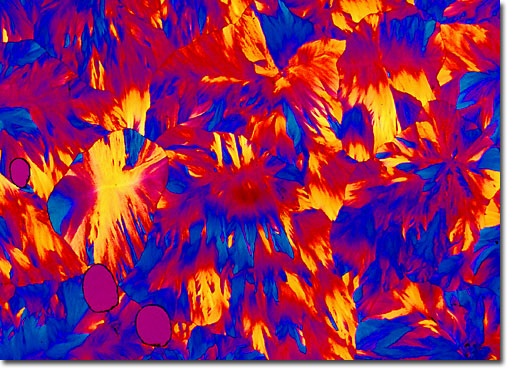
Carbofuran
View a second image of carbofuran.
|
Carbofuran is a member of the carbamate class of pesticides derived from the basic carbamic acid moiety. The mode of action of this pesticide is similar to that of the organophosphates, which act by inhibition of the enzyme cholinesterase. Carbamates were first introduced in 1951 by Geigy Chemical Company in Switzerland, but found little use due to low effectiveness and relatively high cost. Later studies indicated that the N-methyl carbamates were much more toxic to insects. Carbofuran is a plant systemic and has a high water solubility, which allows the pesticide to be taken into the roots or leaves. It is also a very promising nematicide, being registered as a nematicide for alfalfa, tobacco, peanuts, sugarcane, and possibly soybeans, cotton, grapes, and grains. The carbamate has a relatively short residual lifetime, rendering it useful on forage and vegetable crops. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|