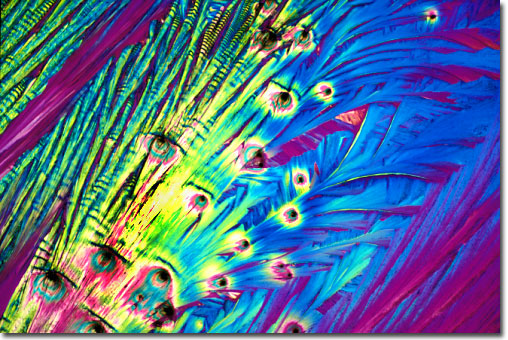
Cysteine
|
Cysteine is only incorporated into proteins at the rate of 2.8 percent relative to the other amino acids, but the unique thiol side chain of this amino acid is often heavily involved in the three-dimensional stability of proteins and enzymes. The side chain is also often involved in the chemistry occurring at the active sites of many enzymes. Cysteine is also critical to the metabolism of a number of essential biochemicals including coenzyme A, heparin, biotin, lipoic acid, and glutathione. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|