alpha-Tocopherol (Vitamin E)
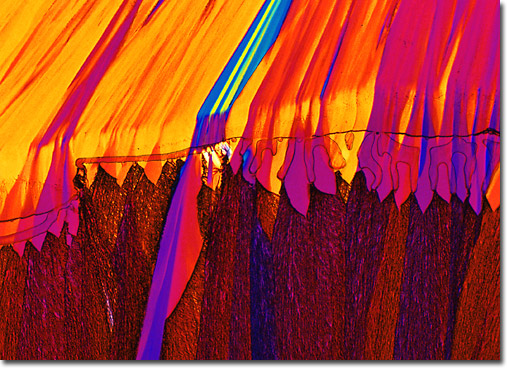
View a second image of vitamin E.
|
Vitamin E was the fifth vitamin discovered when researchers found that a dietary deficiency in laboratory rats produced fetal death in pregnant females. The name "tocopherol" was derived from the Greek words for childbirth (tos), to bring forth (phero), and the chemical designation for an alcohol (ol). Vitamin E acts as a co-enzyme in cellular membranes and serves as a scavenger for free radicals that are destructive to the membrane and internal cellular components. Natural sources of vitamin E are vegetable oils, sunflower seeds, almonds, and peanuts. |
© 1995-2025 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Conditions set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
|